Tank vs. Tankless Water Heaters in Southern California
Tank vs tankless water heaters in southern california

Tank vs Tankless Water Heaters in Southern California
Choosing between a tank-style water heater and a tankless water heater is a common decision for homeowners in Southern California. Both systems are designed to provide reliable hot water, but they operate very differently and offer distinct advantages depending on household size, water usage patterns, energy costs, and installation conditions. Understanding these differences helps homeowners make informed decisions that balance comfort, efficiency, and long-term value.
Southern California presents unique considerations for water heating systems. Mild winters, higher utility costs, strict efficiency standards, and a large number of slab foundations and garage installations all influence which system may be the better fit. What works well in one region or home may not be ideal in another, making it important to evaluate tank and tankless systems in the context of local conditions.
At their core, tank water heaters store and heat a fixed amount of water, while tankless systems heat water on demand. Each approach has implications for performance, installation complexity, and maintenance requirements.
Tank Water Heaters: Pros, Cons, and Best Use Cases
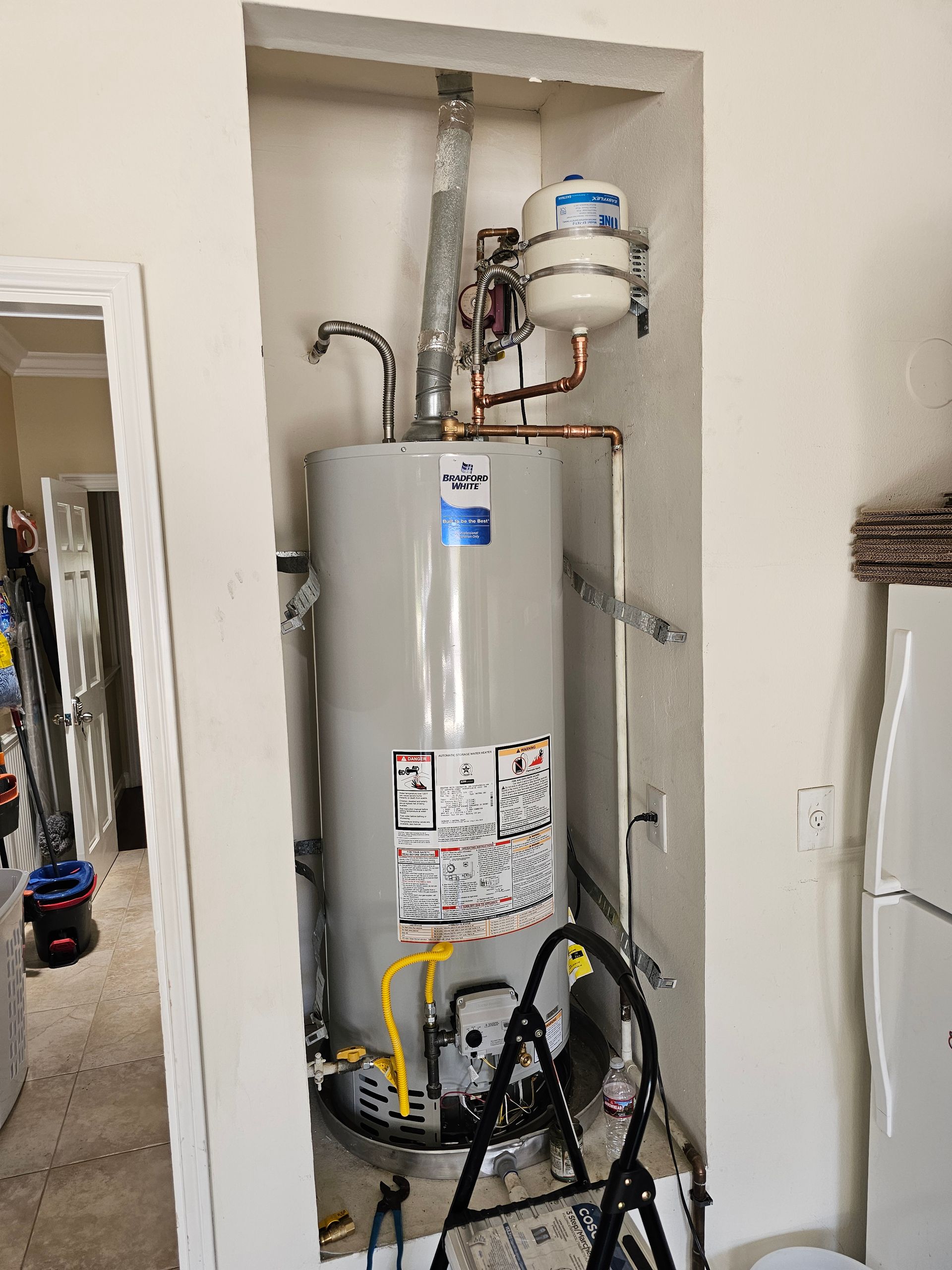
Tank water heaters are the traditional and most widely used option. They store hot water in an insulated tank, typically ranging from 30 to 75 gallons, and keep it heated until needed. When hot water is used, cold water enters the tank and is heated to replace it. This simple design makes tank water heaters reliable, affordable, and easy to service.
In Southern California homes, tank water heaters are often a practical choice due to lower upfront cost and compatibility with existing plumbing and gas or electrical systems. They perform well in homes with predictable water usage and are generally quicker to install or replace. Repairs and parts are widely available, and maintenance requirements are straightforward.
However, tank systems have limitations. Once the stored hot water is depleted, occupants must wait for the tank to reheat, which can be inconvenient for larger households. They also consume energy continuously to maintain water temperature, leading to standby energy losses. Over time, sediment buildup inside the tank can reduce efficiency and shorten lifespan if not properly maintained.
Tankless Water Heaters: Pros, Cons, and Best Use Cases
Tankless water heaters, also known as on-demand systems, heat water only when it is needed. Instead of storing hot water, they use powerful heating elements or burners to instantly heat water as it flows through the unit. This design allows for a continuous supply of hot water without running out, making tankless systems attractive for homes with higher or irregular demand.
In Southern California, tankless systems benefit from relatively moderate incoming water temperatures, which can improve efficiency and performance compared to colder regions. They are often chosen for energy efficiency, space savings, and longer equipment lifespan. Wall-mounted designs free up floor space, which is valuable in garages, closets, or compact utility areas.
Despite these advantages, tankless systems require careful planning. Installation costs are typically higher due to the need for upgraded gas lines, electrical service, venting modifications, or condensate drainage. Performance depends on proper sizing, and multiple simultaneous hot water demands can exceed the system’s capacity if not designed correctly. Maintenance is also more involved, particularly in areas with hard water, where periodic descaling is essential.
Comparing Efficiency, Cost, and Longevity
When comparing tank and tankless water heaters, efficiency is often a key factor. Tankless systems generally use less energy overall because they eliminate standby heat loss, but actual savings depend on usage habits and energy rates. In Southern California, where utility costs are higher, efficiency gains can be meaningful over time.
Upfront cost is another major consideration. Tank water heaters are less expensive to purchase and install, making them a popular choice for budget-conscious homeowners or rental properties. Tankless systems have higher initial costs but may offer longer service life and lower operating costs when properly maintained.
Longevity also differs between the two. Tank water heaters typically last 8 to 12 years, while tankless systems can last 15 to 20 years or more. However, longevity depends heavily on water quality, maintenance, and installation quality. Choosing the right system involves balancing immediate costs with long-term performance and reliability.
Which Option Is Right for Southern California Homes?
There is no one-size-fits-all answer when choosing between tank and tankless water heaters in Southern California. Smaller households with moderate water usage may find a tank system perfectly adequate and cost-effective. Larger households, homes with luxury fixtures, or properties seeking maximum efficiency may benefit from a properly designed tankless system.
Local factors such as available gas supply, electrical capacity, installation location, and water hardness should all be evaluated before making a decision. In some cases, upgrading supporting infrastructure can outweigh the benefits of switching systems. Consulting with a qualified professional ensures the system is sized correctly, installed safely, and aligned with local requirements.
Ultimately, both tank and tankless water heaters can perform well in Southern California when chosen thoughtfully and installed correctly. Understanding how each system works and how it fits your home’s needs is the key to long-term satisfaction and dependable hot water. If you would like more information, you can speak to a licensed technician!